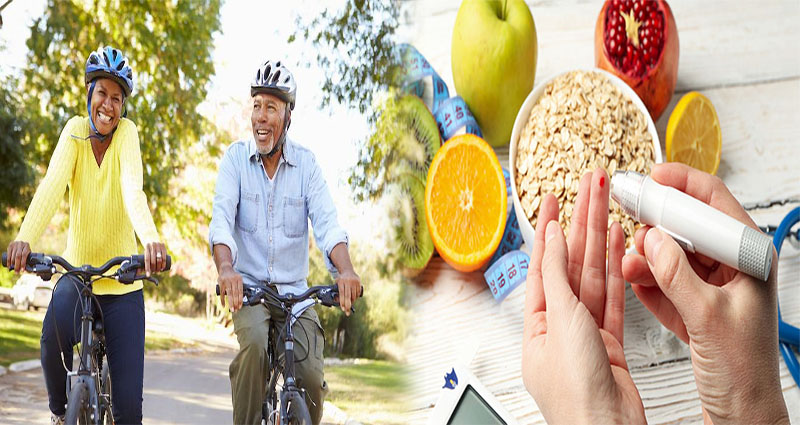
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. While there is no cure for diabetes, lifestyle adjustments can help individuals with type 2 diabetes manage their condition and prevent complications. Making changes to your diet, physical activity, and overall lifestyle can not only help you manage your diabetes but also improve your overall health and quality of life. In this article, we will explore some lifestyle adjustments that can aid in diabetes control.
1. Healthy Eating
Healthy eating is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. Individuals with type 2 diabetes should focus on consuming a diet consisting of whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is recommended to limit your intake of sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated and trans fats. A registered dietitian can help you create a personalized meal plan to meet your specific nutritional needs and diabetes management goals.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity plays a significant role in managing diabetes. Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood glucose levels, and promote weight loss or weight maintenance. Adults with type 2 diabetes should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week and perform strength-training exercises at least two days per week. It is essential to speak with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
3. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is critical in diabetes control, as excess weight can affect insulin resistance and increase the risk of complications. Losing even a small amount of weight can improve blood glucose control and reduce cardiovascular risk factors. Accomplishing weight goals can be achieved through diet, physical activity, and stress management.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on diabetes management by elevating blood glucose levels and contributing to poor lifestyle choices like overeating or inadequate physical activity. Consider incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or massages to help manage daily stressors.
5. Sleep Hygiene
Getting adequate amounts of quality sleep is fundamental in diabetes management. It is advisable to aim to get seven to eight hours of sleep each night to help regulate hormones and blood glucose levels. Sleep hygiene consists of limiting caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, creating a comfortable sleep environment devoid of distractions, and setting a consistent sleep schedule.
Diabetes management is primarily reliant on making lifestyle adjustments. Following a healthy eating plan, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight range, stress reduction, and quality sleep is paramount in improving diabetes management. Small incremental changes can reap positive rewards in diabetes control and overall health. If you have questions regarding a personalized plan to better manage and control diabetes, consult your physician or a registered dietitian. Together, with regular monitoring and medical supervision, type 2 diabetes can be effectively managed, resulting in healthier and more fulfilling lives.